Unlike traditional trading, where investors can only trade with the capital they possess, Crypto margin trading enables them to access larger positions with a smaller initial investment.
The 24/7 open cryptocurrency market embraces a lot of opportunities for traders where they can access live trading on thousands of crypto assets. Unlike traditional stock exchanges, crypto exchanges are open and simultaneously enable cryptocurrency trading across different countries. These exchanges provide crypto traders with various trading services such as spot trading, margin trading, futures trading, or simply buying and selling cryptocurrencies.
This article will elaborate on Crypto Margin Trading and provide an in-depth understanding of isolated and cross margins. Let’s get started with clearing the concept of margin trading.
What is Crypto Margin Trading?
Crypto Margin trading is a method in which traders can borrow funds from the exchange and increase their trade size. Traders must use initial collateral as a margin to borrow additional funds from the exchange. This benefits traders with a significantly increased size of position on a limited amount of funds.
While margin trading enables buying larger sizes of trading using low collateral, it eventually increases profitability by a significant amount. However, this also comes with a severe risk of losing the initial margin. For instance, if a trader opens a trade with a $100 margin and 10x leverage, his trade size will be $1000, and he will profit on $1000 rather than a $100 margin. But if somehow the trade’s liquidation price is hit, he will lose $100.
Also read: How Crypto Futures Trading Differs From Spot Crypto Trading?
This above example highlights that Margin Trading is quite different from spot trading, where traders can only buy assets from their account balance. Spot trading is considered safe as it has no liquidation risks, while margin trading is much riskier, but profitability is higher.
The following are the terms associated with crypto margin trading.
Leverage
Leverage is the measure of funds borrowing in margin trading. It usually ranges between 1x to 100x, where 100x leverage means a trader can borrow 100 times the amount from the exchange to open a trade. For example, if a trader has a margin of $100 and uses 100x leverage, the trade size will be $100,000.
Liquidation Price
Liquidation price is a marked price of the underlying asset on which the trade position is forcefully closed, and the trader loses their margin. Liquidation usually occurs when asset’s price fluctuates too broadly within a short period of time. As such, the recent sharp drop in Bitcoin price caused over $679 million of liquidation in 24 hours.
Initial Margin And Maintenance Margin
Initial Margin is the fund that a trader must provide in order to open the trade. This is usually required as collateral to set leverage. The maintenance margin is a separate amount to support the trade and keep it away from hitting liquidation.
As we now have a proper understanding of margin and its use in crypto trading, we can move further to understand its types. Let’s get into it;
Types of Margin in Crypto Trading
In the realm of crypto margin trading, margin trading typically falls into two primary categories:
- Isolated Margin
- Cross Margin.
These distinctions play a crucial role in determining the level of risk and exposure involved in leveraging borrowed funds for trading activities.
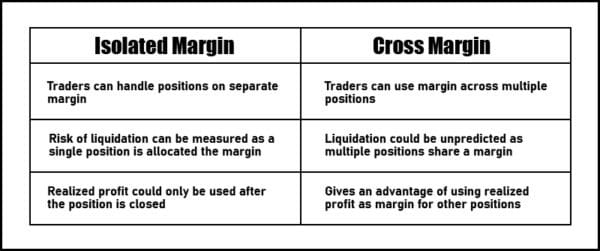
Isolated Margin
Isolated margin is the fund allocated to an individual trading position. This fund is managed and used for that particular position only, and the profit and loss (PnL) amount in maintenance margin will only be subjected to this position. When in the liquidation scenario, the trader will only lose the margin allocated to this single position.
For example, let’s say Mark is a trader with a balance of $1000 in his account. He opens a futures position of $5000 on 10X leverage while selecting an isolated margin. In this trade, he will only have to use the margin of $500 from his account. Now, if the trading position reaches the liquidation stage, it will only risk a loss of $500 and not the whole account balance.
The position opened using Isolated Margin can be modified, and the margin amount can be adjusted. For example, when the traditional position nears liquidation, the liquidation price can be lowered by allocating an additional margin.
Cross Margin
The trading position using Cross Margin will be subject to the overall margin balance in the trader’s account. Opposed to Isolated Margin, Cross Margin enabled open positions consider the total maintenance margin account balance.
Here, the margin is shared among several open positions prior to hedging against one another. Most of the cryptocurrency exchanges set open prepositions to cross margin by default. This way, any realized profit and loss will be used as a margin. While this method enables traders to benefit from increased purchasing power, it also poses a significant risk to the margin balance. Cross margin is much beneficial in employing best trading techniques when crypto market sees high volatility.
Cross Margin is used by sophisticated traders with highly sophisticated risk management practices. As an example, Mark opens a futures position with Cross Margin and has a realized profit of $200. He can use this profit to open another position and combine both positions’s PnL. However, he is exposed to such risk that if one position fumbles, it may lead to the liquidation of all others.
Enlist Difference between Isolated Margin and Cross Margin
Advantage of Crypto Margin Trading
Margin trading enables to have a bigger size of portfolios and boosts investment for traders. It opens wide doors for magnifying profits while only requiring minimum capital at the initial level. Margin trading also allows traders to gain instant access to vast funds by deploying sophisticated trading strategies to earn lucrative returns. By not requiring significant upfront capital, this method of trading becomes a good entry point for traders with limited amounts of funds.
Disadvantage Crypto Margin Trading
Margin trading also has disadvantages, and liquidation is one of them. The uncertain market movements and high volatility could result in the loss of funds while trading with a cross margin. Margin trading is subject to higher fees than spot trading, which traders have to pay every time they open or close their positions. It also causes emotional stress to traders as the price of underlying assets could fluctuate too harshly in volatile market times. Using high leverage in crypto margin trading is one of the biggest mistakes new crypto traders and investors make.
Conclusion
Crypto Margin trading is an innovative financial instrument that crypto traders widely use. It provides robust gain opportunities while also posing a significant risk of losing all funds if not used carefully. Most professional traders use margin trading to amplify higher returns and place themselves perfectly in the market. As margin trading possesses severe risk on the capital, one must first learn, understand, and practice before jumping in with 100x leverage.
FAQs
What is Cross Margin?
Cross margin is a mode of margin trading where traders can share margin across multiple open positions.
What is an Isolated Margin?
Isolated margin allows traders to treat each of their positions with separate margins, unlike cross margin, where positions share margin balance.
Is crypto margin trading any good?
Crypto Margin trading provides crypto traders with opportunities to maximize their gains, but it requires knowledge and understanding. The funds can be lost if margin trading positions are not managed sophisticatedly.