Blockchain technology may seem complicated but it is very easy to understand. Introduced by Bitcoin, it is a very simple easily understandable database system.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger that makes recording transactions and managing assets in a corporate network much easier. On a blockchain network, virtually anything of value may be recorded and traded, cutting costs for all parties involved.
Information is the heart of the business and when it is received faster it’s an added benefit. Because it delivers immediate and entirely transparent information kept on an immutable ledger, blockchain is excellent for delivering that information. Orders, payments, accounts, production, and much more may all be tracked using a blockchain network.
The most important aspects of a blockchain consists of distributed ledger technology, immutable records, and smart contracts.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a protocol that allows a decentralised digital database to run securely.
What is decentralization?
The movement of control and decision-making from a centralised entity to a dispersed network is referred to as decentralisation in the blockchain.
Decentralized networks aim to limit the amount of trust that participants must place in one another. Three basic network designs are often examined when developing a centralised, distributed, and decentralised technology solution. Although decentralised networks are frequently used in blockchain technology, a blockchain application cannot simply be classified as decentralised or not.
Decentralization has drawbacks, such as lower transaction throughput, but the benefits of enhanced stability and service levels outweigh the drawbacks.
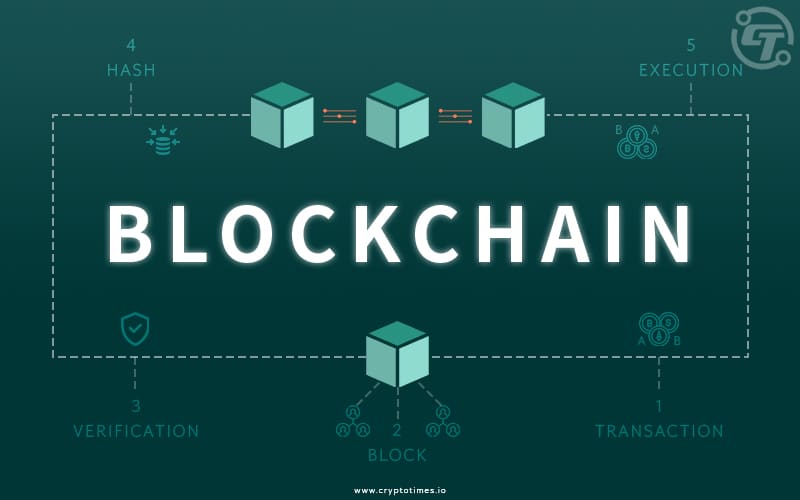
Transaction and storage:
Initially, a transaction is requested and authenticated, then a block is represented indicating that a transaction is created. The block is then sent to every node in the network and the nodes validate the transaction. Further, then the nodes receive a reward for proof of work typically in cryptocurrency. The block is then added to the existing blockchain, and the update is distributed across the network. The transaction is then completed.
Because blockchain is decentralised, there is no single location where it may be stored and hence stored in computers. They are called nodes. Each of the nodes has a copy of the blockchain, which contains all of the network’s transactions. Hence, the blockchain system can be compared to a spreadsheet, with data in each row representing the value of an address.
How is blockchain private and transparent?
Blockchain is private, transparent, and secure all at the same time. That may appear to be an oxymoron, yet it is entirely possible.
Since blockchain exists digitally as a ledger, it can increase the personal security of shoppers and hold businesses accountable. Services on the blockchain protect one’s identity by using cryptography that is both strong and unbreakable. Individual users cannot be traced to public blockchain addresses as a result of this. This makes it more difficult for criminals to gain access to data and ensure that the transactions remain a complete secret.
There’s no denying that blockchain is transforming our understanding of cybersecurity. In the cybersecurity community, transparency is only one of the numerous ways that blockchain may benefit security companies, regular end users, and even governments. It’s not every day that we come across technologies that can both ensure the validity of assaults and make them public. Security companies will be able to provide concrete evidence to back up their claims of performance or efficacy, and individuals will be able to use this information when selecting a cybersecurity solution thanks to blockchain.
How secure is blockchain?
The fundamental goal of adopting a blockchain is to allow people to communicate valuable data in a safe, tamperproof fashion. Because blockchains use complicated arithmetic and novel software rules to store data, adversaries find it incredibly difficult to corrupt them.
Two elements make this system potentially tamperproof: a cryptographic fingerprint and a consensus procedure. A cryptographic fingerprint is unique to each block. A “consensus procedure,” is the process through which network nodes agree on a common history.
The fingerprint, known as a hash, takes a long time and a lot of computational power to create at first. It serves as verification that the miner who added the block to the blockchain performed the computational labour in exchange for a payment. The hashes also function as linkages in the blockchain, with each block including the previous block’s unique hash. The blockchain is tamperproof, or “immutable,” because of this.
Uses of blockchain Technology:
- When it comes to supply chain management, blockchain is especially useful. Businesses should discover inefficiencies in their supply chains and locate products in real time by eliminating paper-based trails.
- The most logical application of blockchain is to speed up the movement of funds from one party to another. Most blockchain transactions can be finalised in a matter of seconds.
- By becoming the go-to for loyalty benefits, blockchain further alters the retail experience. It motivates consumers to return to a specific business to complete their shopping by building a token-based system that pays them. It also reduces the fraud and waste that are typically connected with loyalty rewards systems based on paper or cards.
- Copyright and ownership restrictions for music and other content have become ambiguous in a world with increasing internet access. With blockchain, copyright regulations for digital material downloads are significantly strengthened, guaranteeing that the artist receives a fair share. It also provides musicians and content providers with real-time and transparent royalties distribution data.
- Blockchain allows for digital voting, it is transparent that any regulators would be able to know if any changes made. To make the vote genuinely count, it blends the convenience of digital voting with the immutability of blockchain.
- One of the main purposes of blockchain is to eliminate paper from the mix, as paper trails can be confusing. Instead of papers, blockchain keep titles on its network, providing a transparent image of the transfer and the legal ownership.
- Blockchain may potentially be the ideal method for data backup. It can be a backup source for cloud data centres or any other data.
- The good news is that the medical industry has been moving away from paper for recordkeeping for years. Blockchain technology provides greater security and ease. In addition to maintaining patient records, the patient, who holds the key to these digital records, would have discretion over who has access to that information.
Advantages of blockchain:
- One of the major difficulties in the current industry is transparency. They can use blockchain to create a decentralised network that eliminates the need for a centralised authority, increasing the system’s transparency.
- In comparison to previous platforms or record-keeping methods, blockchain technology employs greater security. The consensus mechanism must be used to agree on any transactions that are ever recorded. The fact that each node has a copy of all transactions ever conducted on the network adds to the security.
- Businesses are currently spending a lot of money to improve their current system’s management. Organizations may save a lot of money by embracing blockchain to reduce costs connected with third-party vendors.
- Companies can use blockchain to focus on building a supply chain that includes both vendors and suppliers. It allows all parties to track the commodities and guarantee that they are not being replaced or misused.
- Blockchain automates time-consuming processes in order to increase efficiency. With the use of automation, it also eliminates human errors.
Disadvantages of blockchain:
- The blockchain is a network that runs on nodes. Although blockchain is a distributed network, it lacks the characteristics that make a distributed computing system so advantageous to businesses.
- Blockchains are not as scalable as their centralised counterparts. Simply put, the more users or nodes that join the network, the greater the odds of it slowing down.
- It employs the Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm, which entrusts the hard work to the miners. The miners solve problems every time the ledger updates with a new transaction, which requires a lot of energy. The significant energy consumption renders these complicated mathematical problems unsuitable for real-world applications. Hence, it consumes too much energy.
- Immutability of data has always been one of the blockchain’s main drawbacks. Another issue is that data cannot be withdrawn once it has been written.
- Although other platforms are less safe than blockchain technology. This does not imply that it is not entirely safe.
- The underlying cost of putting blockchain technology in place is enormous.
- Blockchain technology has barely been around for a decade. This indicates that it is a novel technology that will take some time to develop.
Also Read: Definition of Bitcoin and Why do People Use Bitcoin?
Future of blockchain technology:
- Blockchain is a solution to many difficulties these days, ranging from crypto enthusiasts to business minds. The issue could be one of data security or smart data movement.
- Blockchain helps marketing benefit considerably. One can choose whom he wants to target and save money.
Conclusion:
Despite all of the criticism and flaws, the technology is worth considering. Blockchain still provides firms with cost savings, increased productivity, and competitive advantage.